LYMPHATIC FILARIASIS (LF)
Back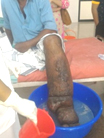 Lymphatic Filariasis (LF), commonly known as elephantiasis is a disfiguring and disabling disease, usually acquired in childhood. In the early stages, there are either no symptoms or non-specific symptoms. Although there are no outward symptoms, the lymphatic system is damaged. This stage can last for several years. Infected persons sustain the transmission of the disease. The long term physical consequences are painful swollen limbs (lymphoedema or elephantiasis). Hydrocele in males is also common in endemic areas.
Lymphatic Filariasis (LF), commonly known as elephantiasis is a disfiguring and disabling disease, usually acquired in childhood. In the early stages, there are either no symptoms or non-specific symptoms. Although there are no outward symptoms, the lymphatic system is damaged. This stage can last for several years. Infected persons sustain the transmission of the disease. The long term physical consequences are painful swollen limbs (lymphoedema or elephantiasis). Hydrocele in males is also common in endemic areas.
Due to damaged lymphatic system, patients with lymphoedema have frequent attacks of infection causing high fever and severe pain. Patients may be bed-ridden for several days and normal routine activities become difficult. Such attacks not only cause acute physical suffering but also directly impede the earning capacity of the individual. Lymphatic filariasis is estimated to be one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. Elimination of the disease is an important tool for poverty alleviation and economic development.